IP Packets Addresses Routers And Networks Course
Description
Set to HD and full screen... or watch in full quality at teracomtraining.com: http://www.teracomtraining.com/online-courses-certification/samples/course-l2113-introduction-ip-packet-networks-addresses-and-routers.htm
CTNS Course L2113 IP Networks, Routers and Addresses: Introduction
Packet Networks • Routers & Routing • IP Address Classes • DHCP & NAT • IPv6
Welcome to Teracom's Online Course "IP Networks, Routers and Addresses".
This free online IP network training course lesson is the introduction to the course.
This is the fifth course in the CTNS Certification Package, a set of six courses plus Certified Telecommunications Network Specialist (CTNS) certification from the Telecommunications Certification Organization (TCO). It is the third course in the shorter IP-specific CIPTS Certification Package.
This course could also be called "Layer 3", as it is all about Layer 3 of the OSI model: the network layer, and in particular, IP packet networks.
Packet networks embody two main ideas: bandwidth on demand and packet switching.
First, we'll recap channelized TDM and its limitations, then understand statistical TDM or bandwidth on demand.
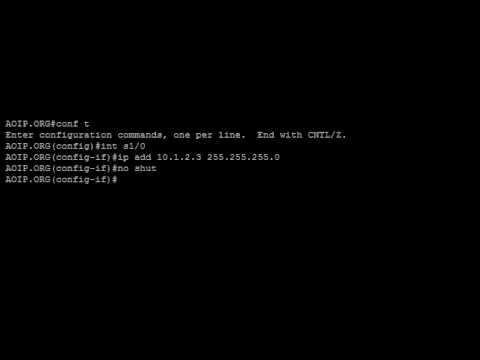
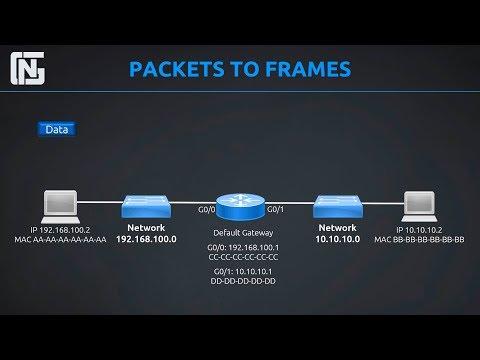
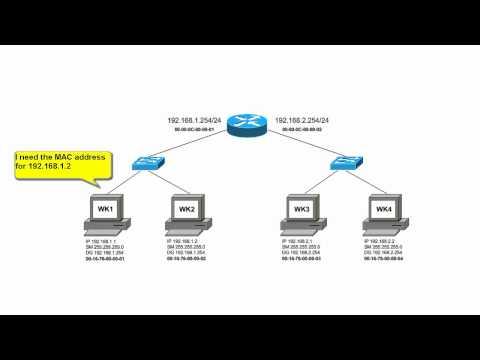
Next, we'll understand how routers implement the network with packet switching, that is, relaying packets from one circuit to another, and how routers are a point of control for network security. We'll introduce the term Customer Edge (CE), and understand the basic structure and content of a routing table.
Then we'll cover the many aspects of IP addressing -- needed to be able to do the packet switching: IPv4 address classes, dotted decimal notation, static vs. dynamic addresses, DHCP, public vs. private addresses, Network Address Translation, and finish with an overview of IPv6 and IPv6 address allocation and assignment.
The objective of this course is to develop a solid understanding of IP. After taking this course, you will be up to speed on the fundamental principles of packet networks: bandwidth on demand, also known as overbooking or oversubscription, and packet forwarding. You will know the IP packet format and how IP addresses are allocated, assigned and displayed. You will know the difference between static and dynamic addresses, public and private addresses and how Network Address Translation works. An additional objective is to become familiar with the basics of IPv6.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this course, you will be able to explain:
- The concept of statistical multiplexing, also known as oversubscription, overbooking and bandwidth on demand, why and how it can be implemented and its benefits.
- What a private network is
- What a router is and how it implements the network by connecting data links
- How routers move packets between broadcast domains, including VLANs
- How routers also act as a point of control for traffic, called packet filtering
- The basic structure and contents of a routing table
- The Customer Edge
- IPv4 address blocks: Class A, Class B and Class C, and dotted-decimal notation
- Static addresses and dynamic addresses, and how and why DHCP is used to assign both
- Public addresses and private addresses, how, why and where each is used
- Network Address Translation for interfacing domains where public addresses are used with those where private addresses are used
- The improvements and changes between IPv4 and IPv6, and
- The types of IPv6 addresses, how IPv6 addresses are allocated to ISPs then assigned to users, and how each residence gets 18 billion billion IPv6 addresses.
List of Lessons
Lesson 1. Course Introduction (this one).
Lesson 2. Review: Channelized Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)
Lesson 3. Statistical TDM: Bandwidth-on-Demand.
Lesson 4. Private Network: Bandwidth on Demand + Routing.
Lesson 5. Routers
Lesson 6. IPv4 Addresses
Lesson 7. DHCP
Lesson 8. Public and Private IPv4 Addresses
Lesson 9. Network Address Translation
Lesson 10. IPv6 Overview
Lesson 11. IPv6 Address Allocations and Assignment